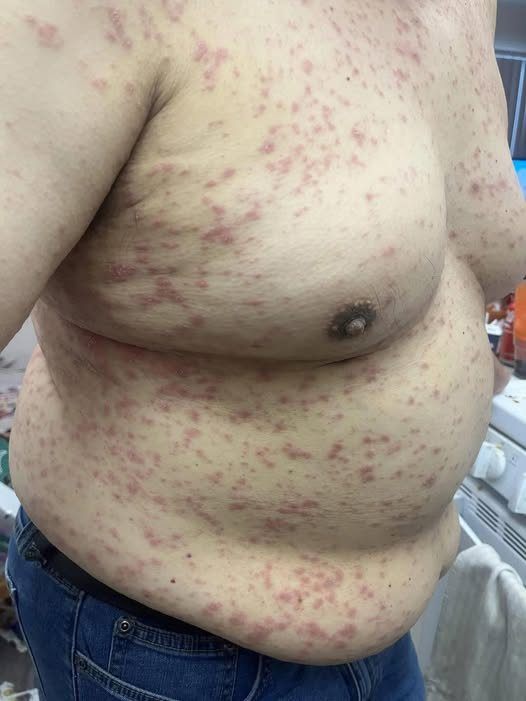
It often begins quietly. A slight itch on the chest. A few red spots that look like a mild allergic reaction. Maybe some scalp itching that feels irritating but manageable. Many people dismiss these early signs, assuming it’s just dry skin, aging, a seasonal change, or something they ate. However, doctors warn that when a widespread, intensely itchy rash appears suddenly — especially in people over 60 — and is accompanied by facial swelling, it can be a serious warning sign that the body is reacting to something potentially dangerous.
Medical specialists explain that full-body rashes combined with severe itching are often linked to allergic or drug-related reactions. As we age, the immune system changes in how it responds to substances. Medications that were tolerated for years without any issue can suddenly trigger strong reactions. Blood pressure medications, antibiotics, pain relievers, and even dietary supplements are among the most common triggers. In many cases, patients do not suspect that a medication they take daily could be the source of the problem.
What makes the situation more concerning is swelling of the face, lips, or eyelids. This indicates that the reaction is not merely superficial. Doctors describe this as a systemic reaction, meaning it involves the entire body. The skin is simply the most visible organ showing signs of distress, but the reaction may also be occurring internally. In such cases, conditions like urticaria (hives) or angioedema are often diagnosed — both of which can escalate rapidly if not treated promptly.
Even if the swelling seems to improve temporarily, physicians warn that symptoms can return suddenly and more severely. Some patients experience repeated waves of rash and itching. In more serious situations, the respiratory system can become involved. Although breathing may feel normal at first, allergic reactions can worsen quickly, making early medical attention critical.
Another frequently overlooked factor is the impact of persistent itching on overall health. Intense itching disrupts sleep, causes fatigue, and increases stress levels. Continuous scratching damages the skin’s protective barrier, raising the risk of bacterial infections. In older adults, healing occurs more slowly, and secondary infections can become serious very quickly.
Dermatologists emphasize that creams and topical treatments alone are often not enough because the root cause is internal, not just on the surface of the skin. Proper treatment requires medical evaluation, a review of current medications, and sometimes stopping or replacing the triggering drug. Antihistamines, corticosteroids, or other medications may be necessary to control the reaction effectively.
Doctors strongly advise against waiting to “see if it goes away.” Many individuals delay seeking care because they do not feel “sick enough” or assume the symptoms are temporary. However, facial swelling is never normal, and a widespread rash with intense itching should not be self-treated at home without professional evaluation. Early intervention can prevent the reaction from worsening and reduce the risk of life-threatening complications.
The message from medical professionals is clear: a sudden, intensely itchy rash covering the body — especially in adults over 60 — should never be ignored, minimized, or diagnosed online. It is a signal that the body is under stress and requires proper medical care. Acting quickly not only relieves symptoms but, in some cases, can save a life.